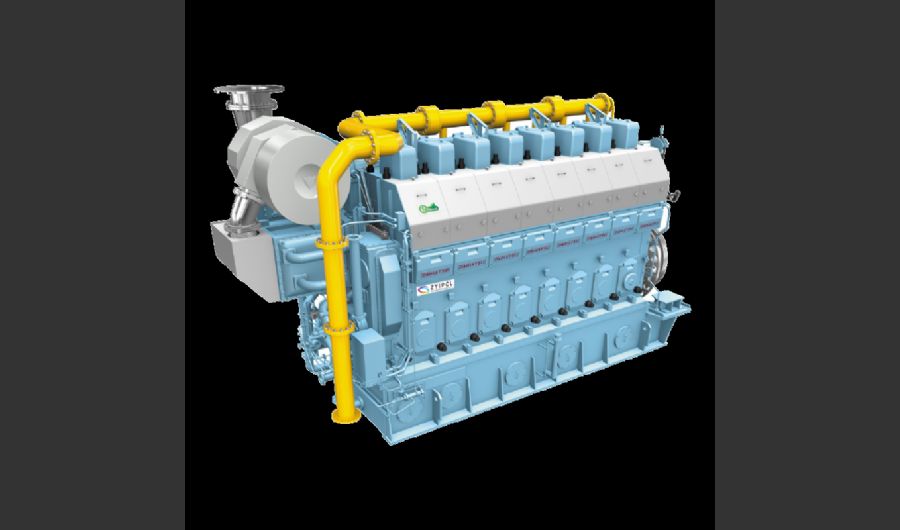
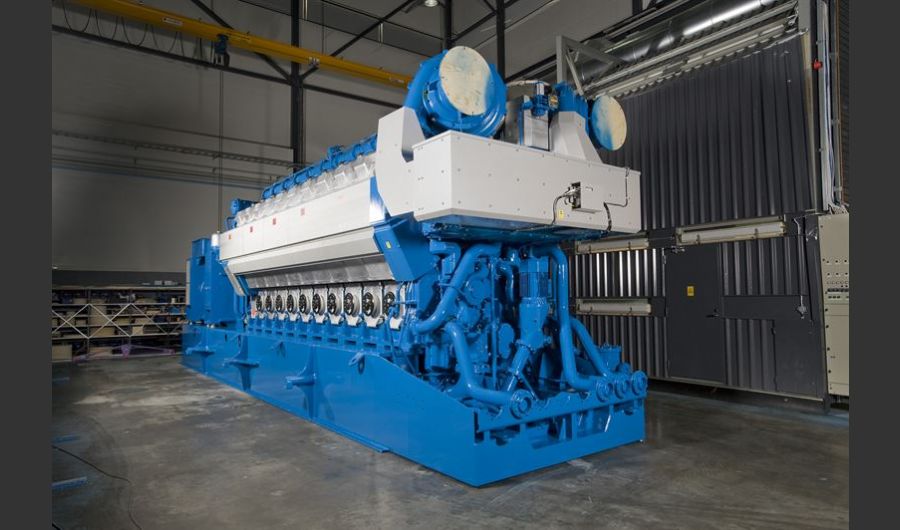
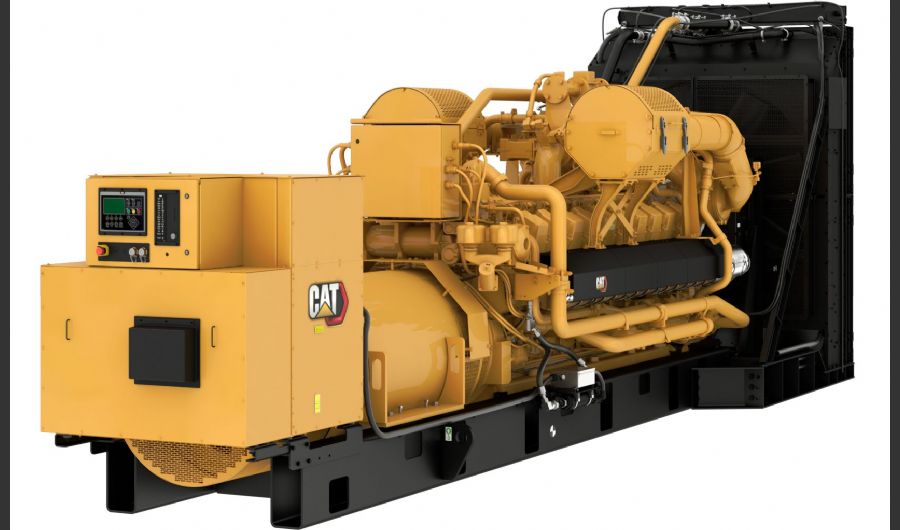
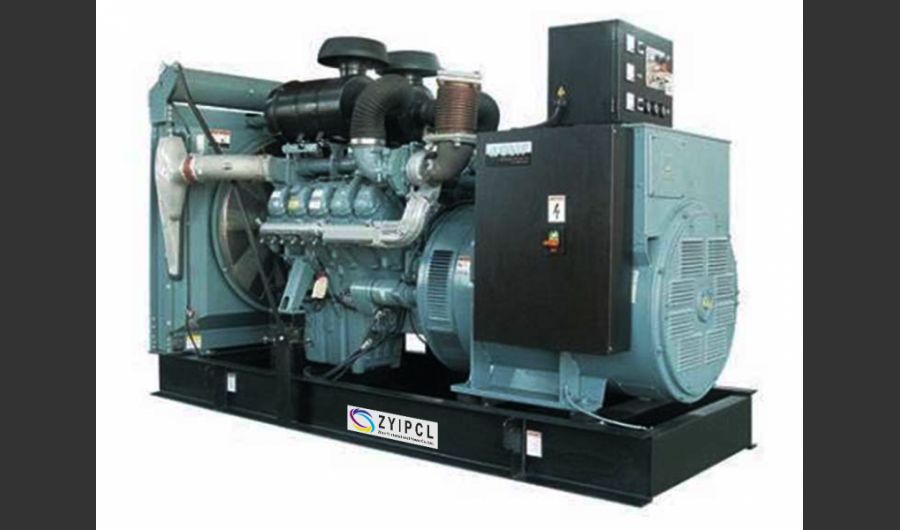
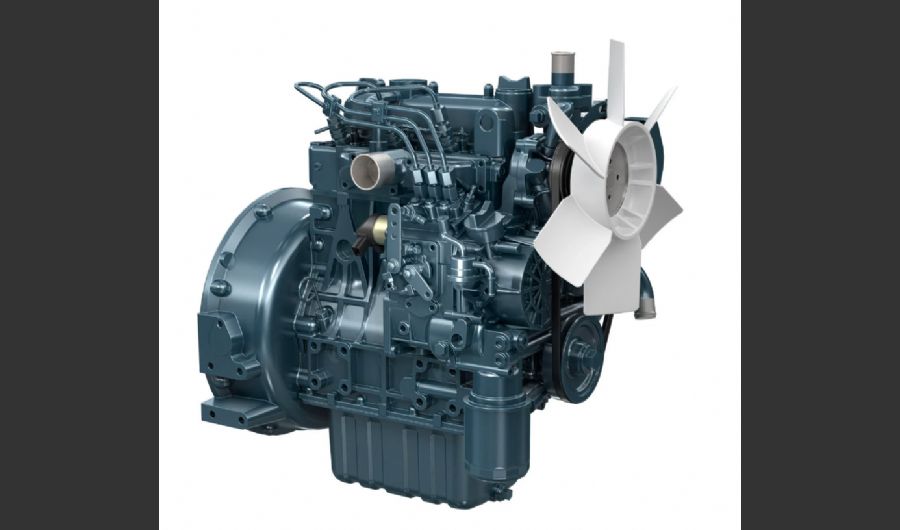
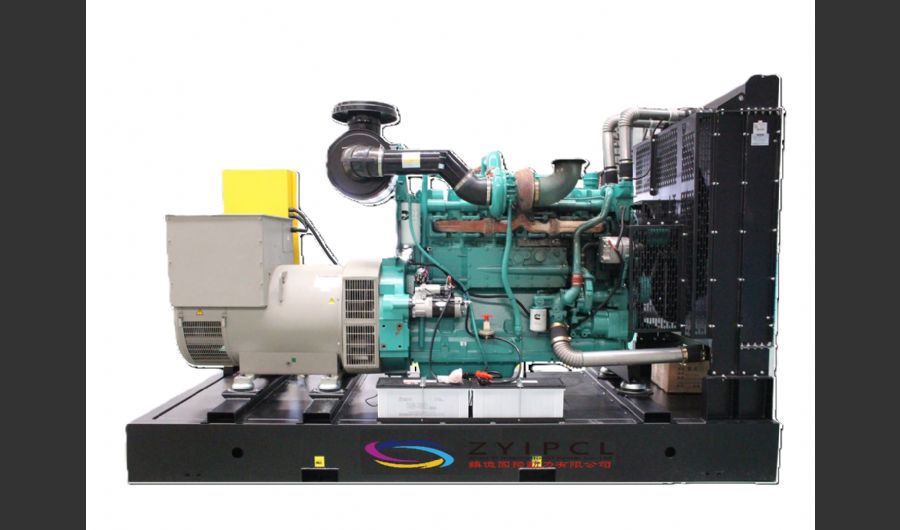
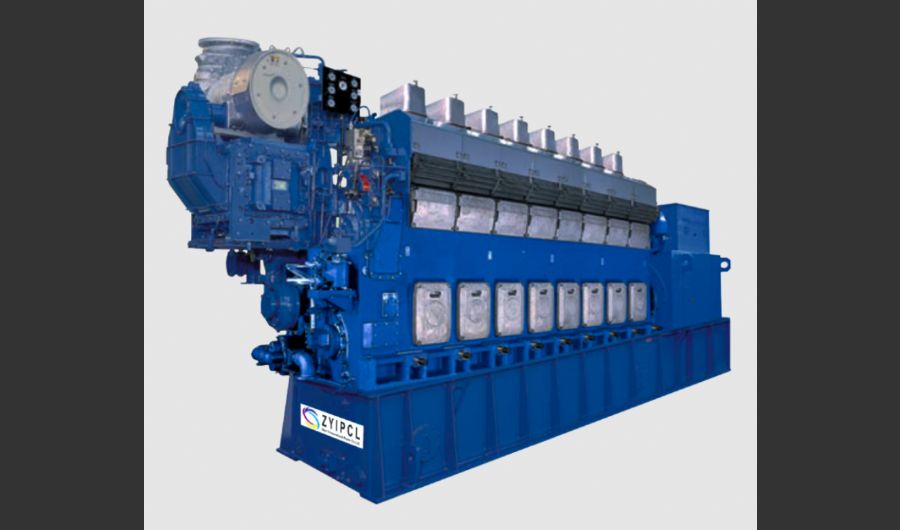
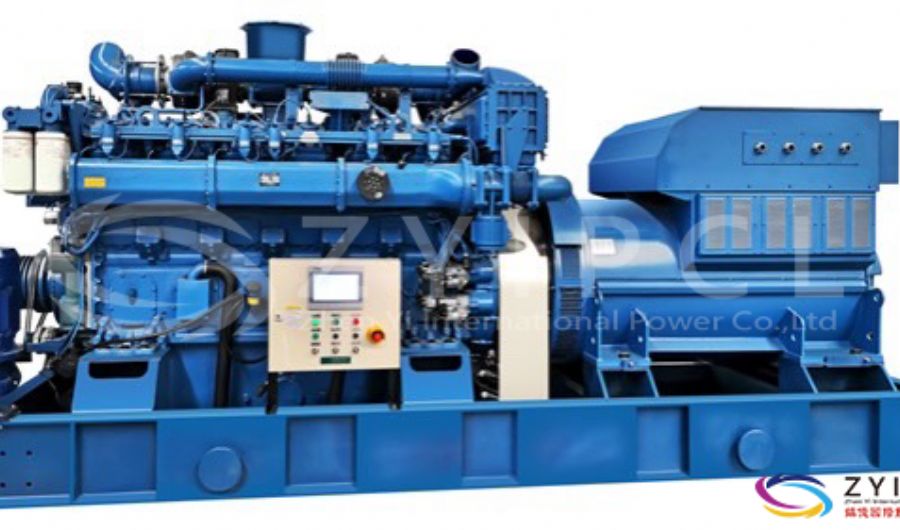
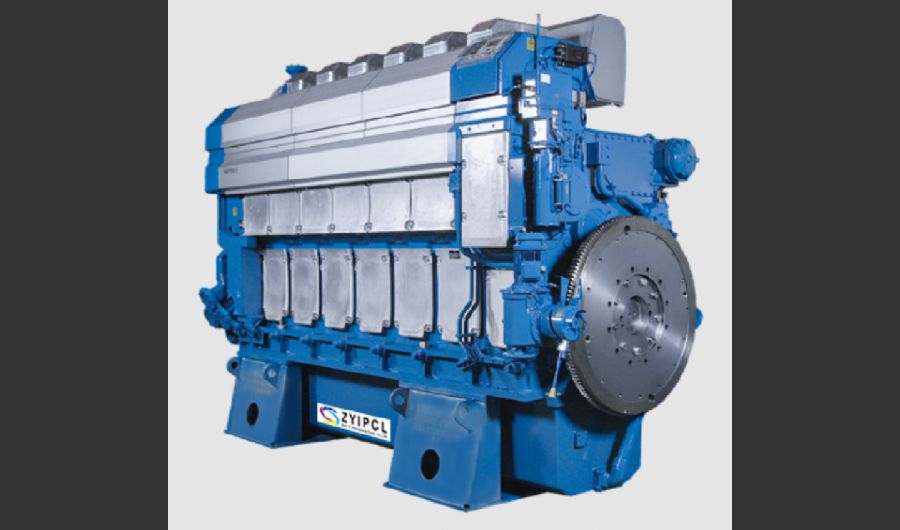
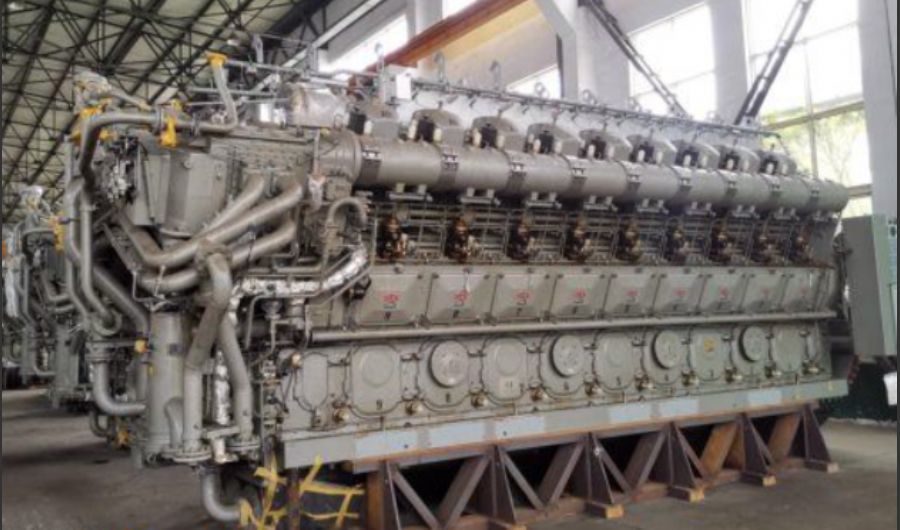
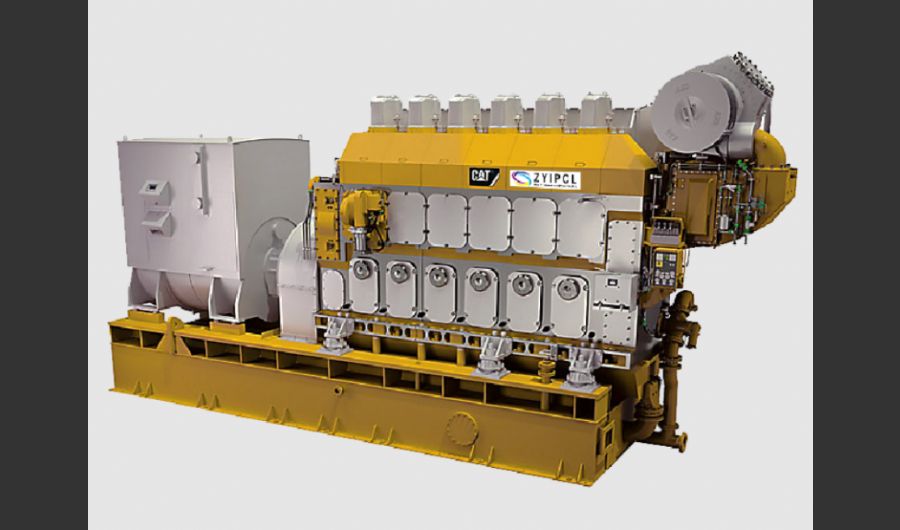
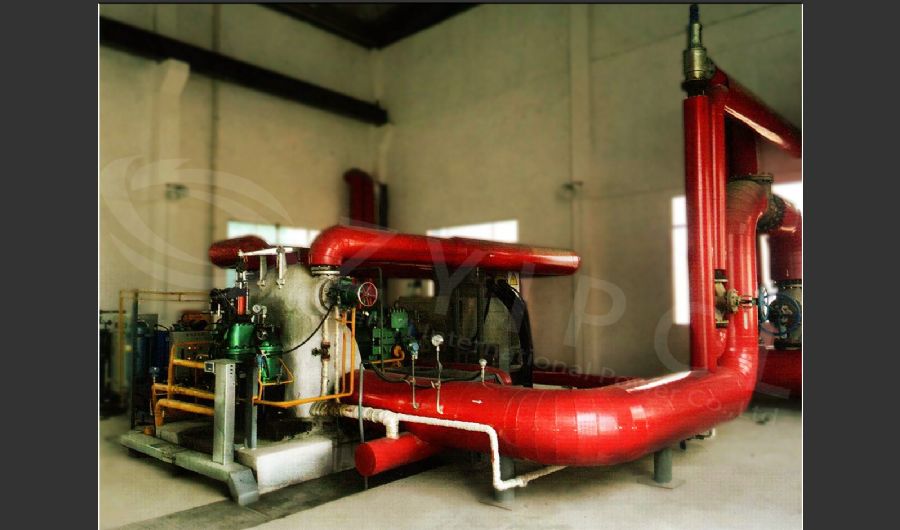
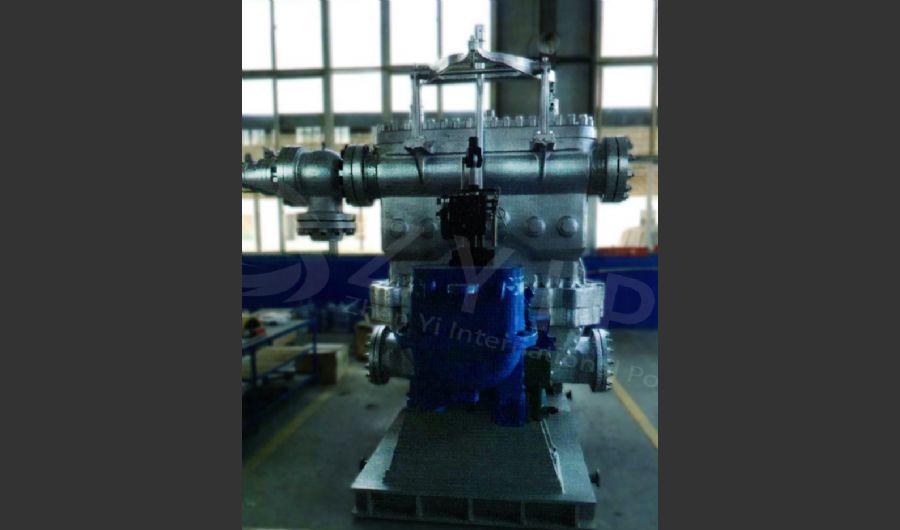
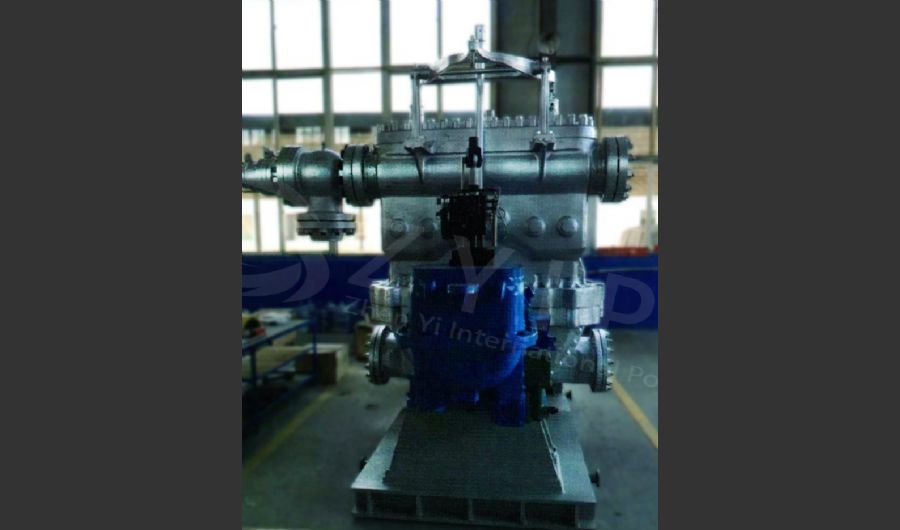
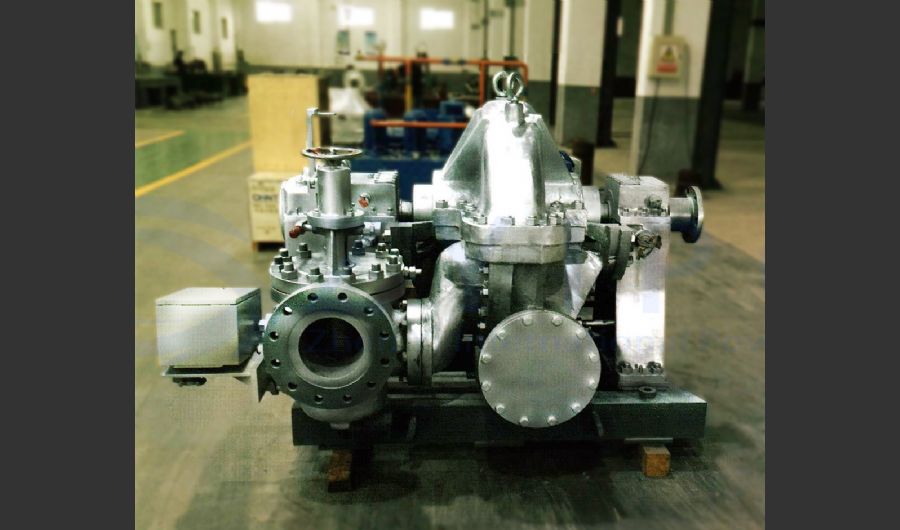
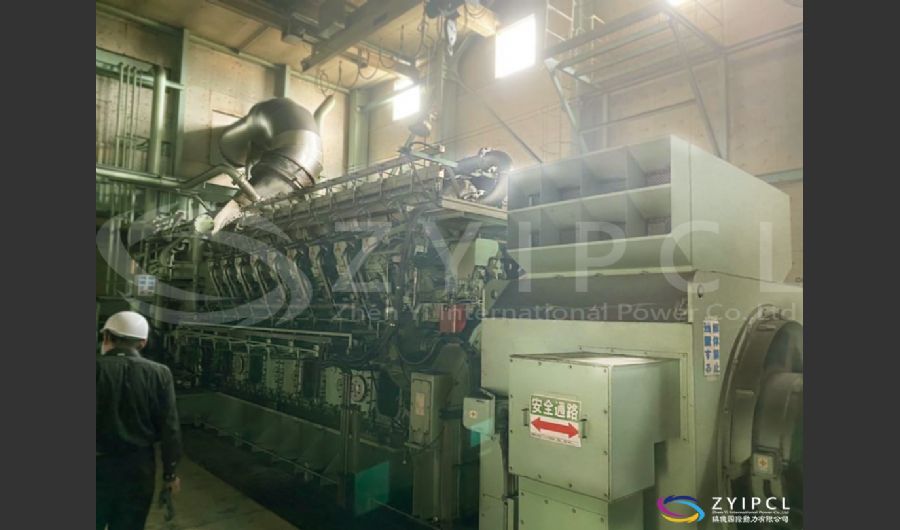
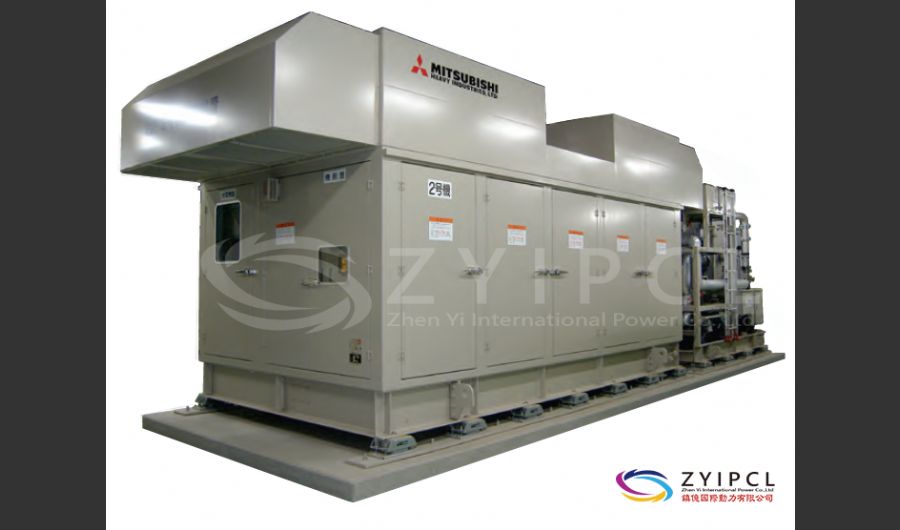
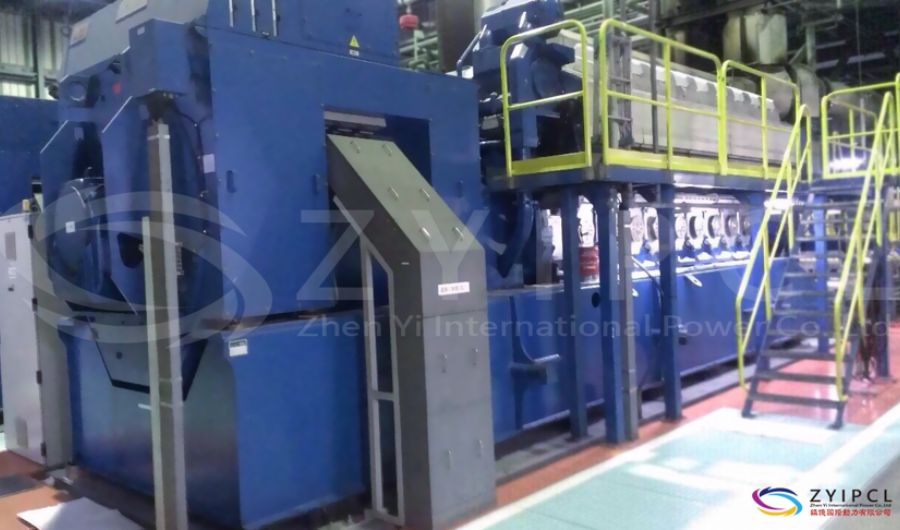
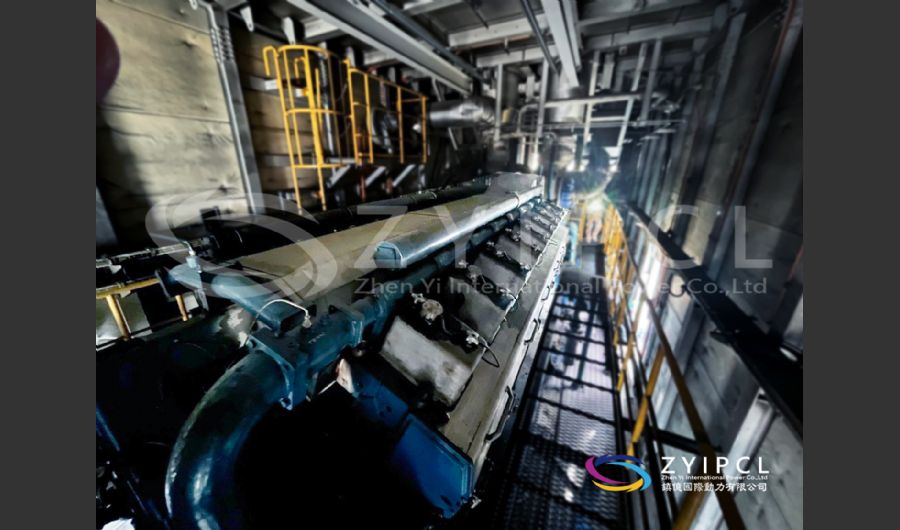
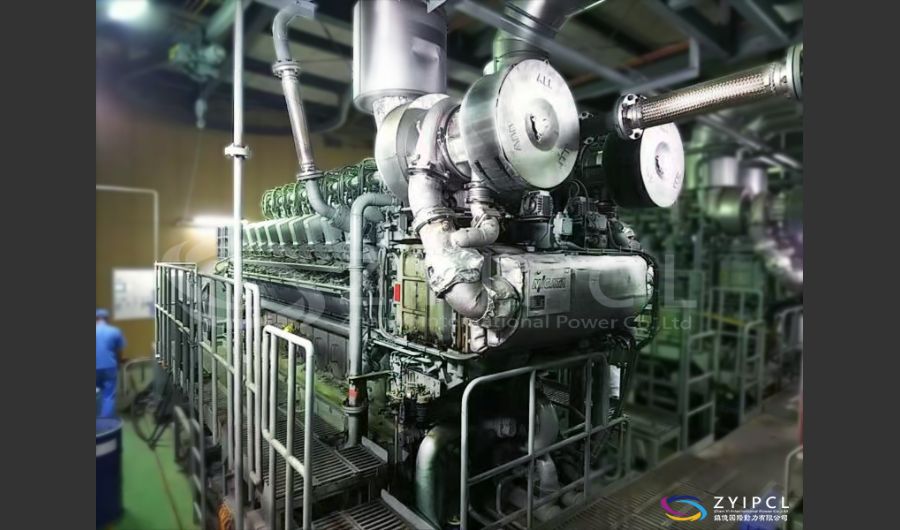
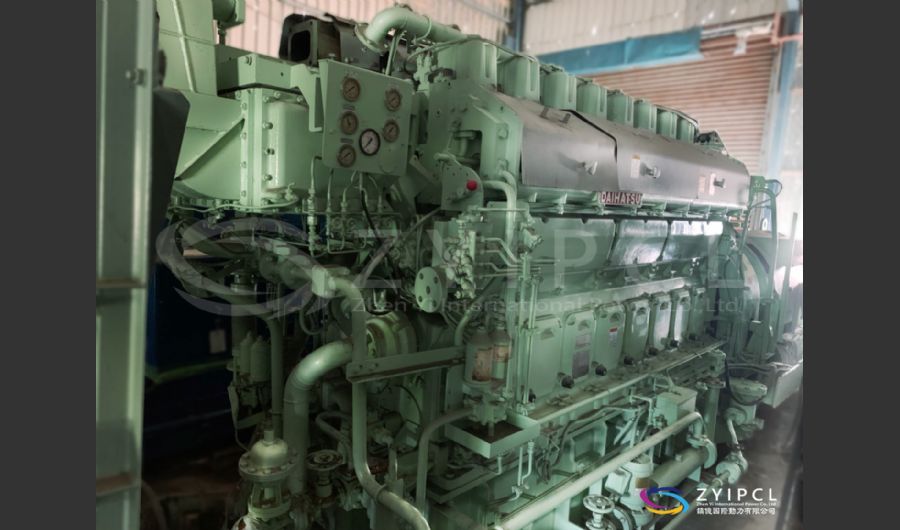
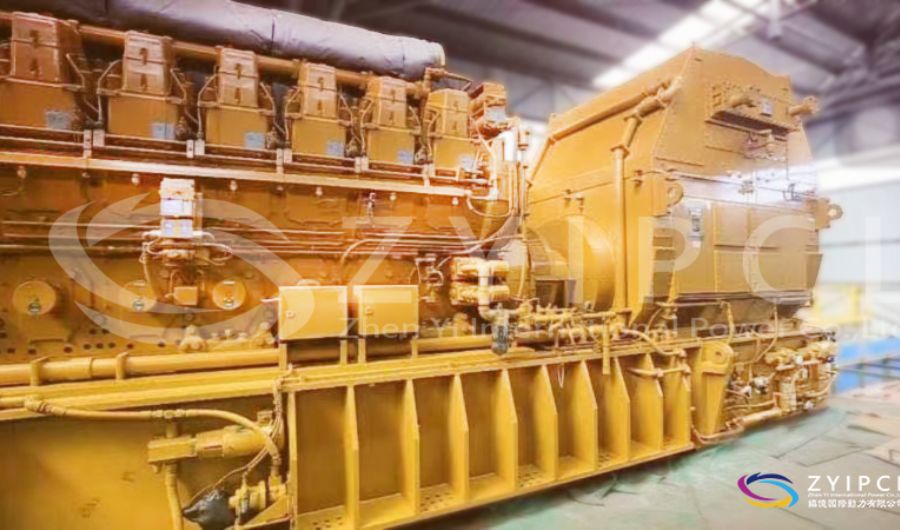
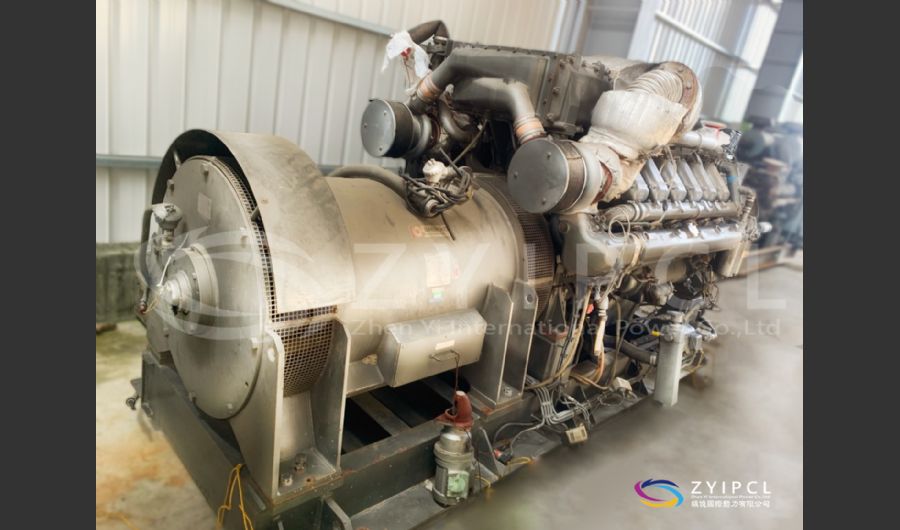
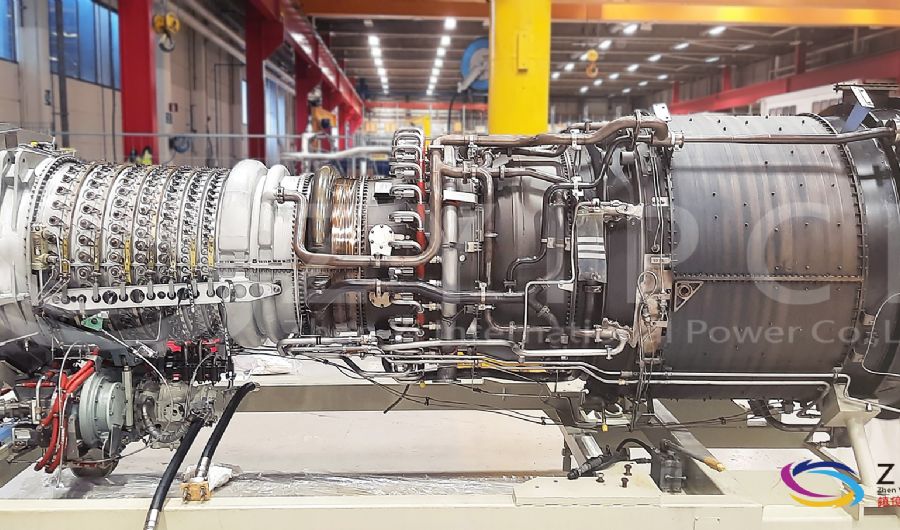
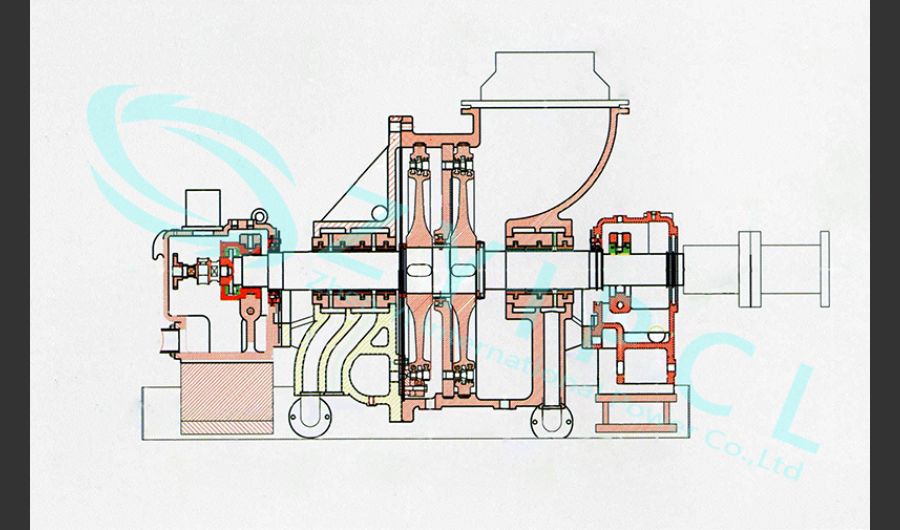
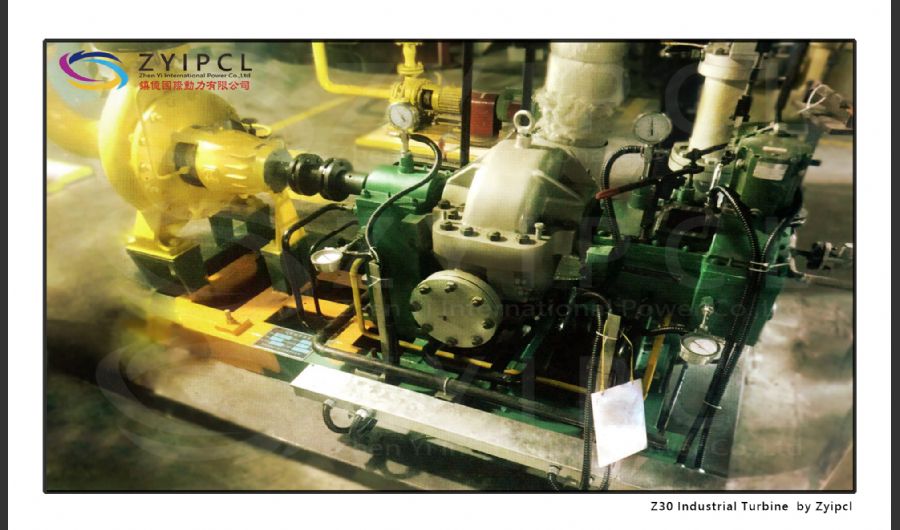
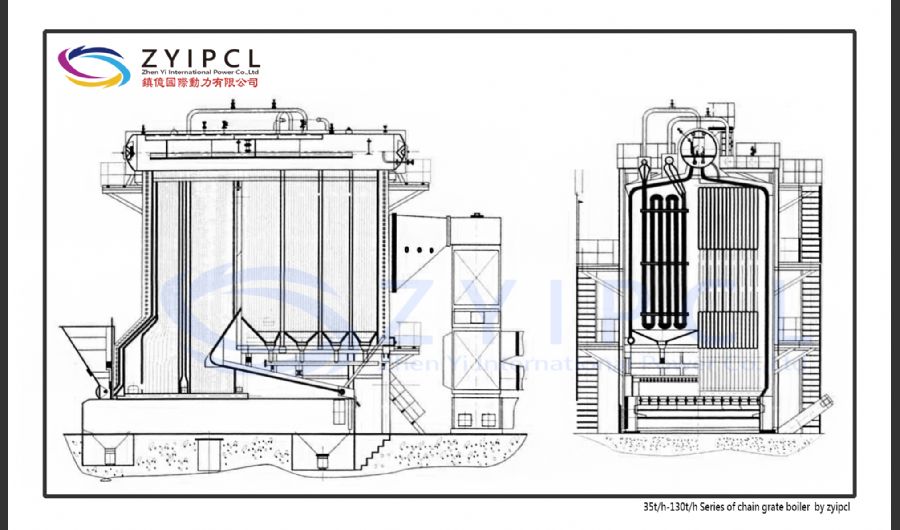
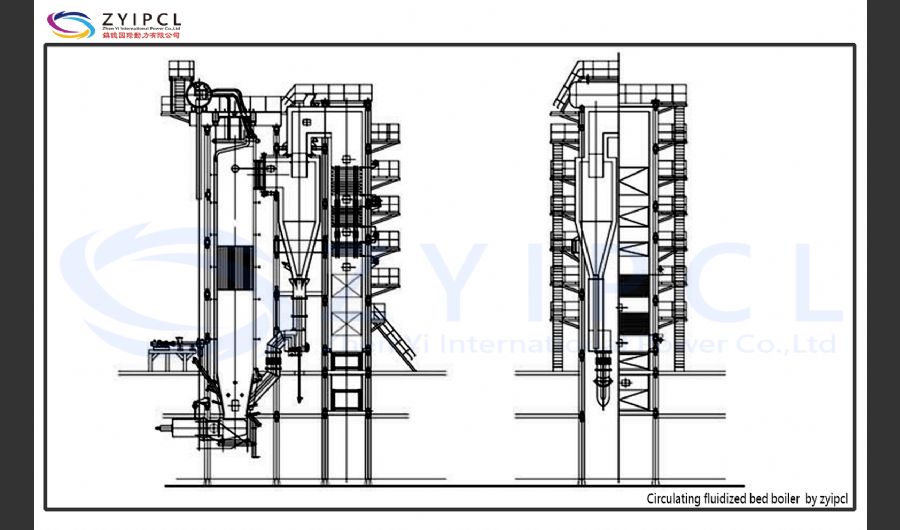
A boiler is a device used to heat water or other fluids to produce steam or hot water for various applications. It plays a crucial role in many industries and heating systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a boiler does and its key components:
Functions of a Boiler
Heat Generation:
- Heating Water: The primary function of a boiler is to heat water. The heat energy is transferred to the water through the combustion of fuel or other heating methods.
- Steam Production: In many systems, especially in power plants and industrial processes, the heated water is converted into steam. This steam is used to drive turbines for electricity generation or for other mechanical processes.
Energy Transfer:
- Heat Exchange: Boilers transfer heat from a fuel source (such as natural gas, oil, coal, or biomass) to the water or fluid inside the boiler. This process involves a heat exchanger that facilitates the transfer of thermal energy.
Pressure and Temperature Control:
- Controlled Environment: Boilers operate under specific pressure and temperature conditions. They are equipped with controls and safety mechanisms to regulate these parameters and ensure safe and efficient operation.
Types of Boilers
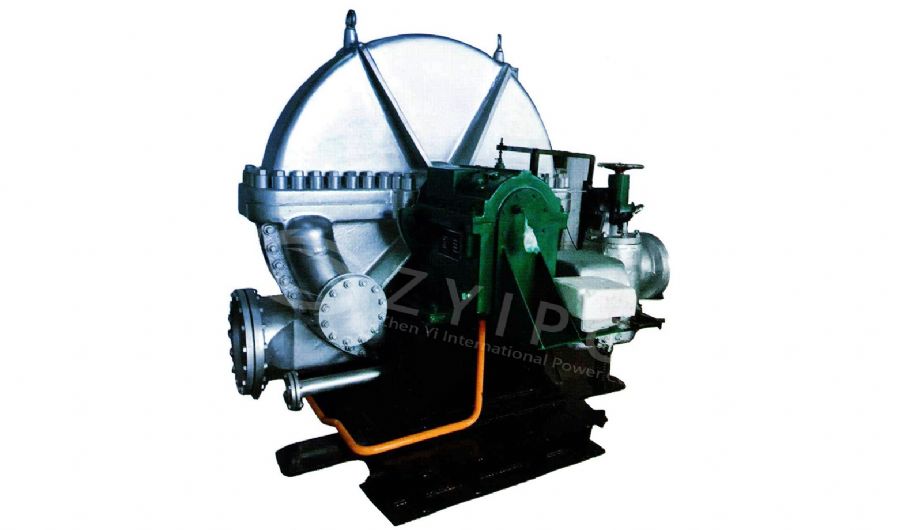
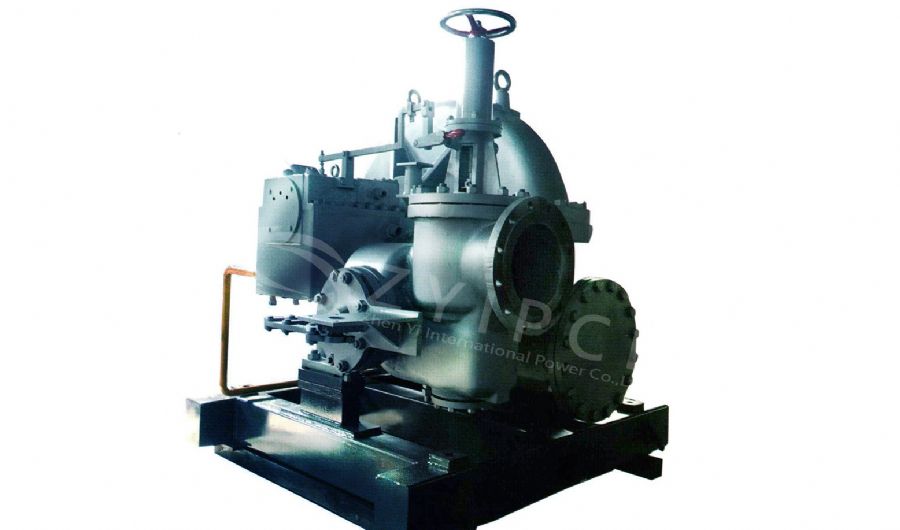
Fire-Tube Boilers:
- Design: In these boilers, hot gases from the burner pass through tubes surrounded by water. The heat from the gases is transferred to the water, producing steam.
- Applications: Common in smaller installations and for applications requiring lower pressure and temperature.
Water-Tube Boilers:
- Design: Water is circulated through tubes that are heated by external combustion gases. This design allows for higher pressure and temperature operations.
- Applications: Used in large industrial and power plant applications where high capacity and efficiency are required.
Electric Boilers:
- Design: Use electrical resistance to heat water. They are typically used in applications where electric power is preferred or where there is no access to other fuel sources.
- Applications: Suitable for smaller-scale or residential applications.
Steam Boilers:
- Design: Designed to produce steam by heating water to its boiling point. The steam is then used for power generation or other processes.
- Applications: Common in power plants, industrial facilities, and heating systems.
Hot Water Boilers:
- Design: Produce hot water for heating purposes or other processes, rather than steam.
- Applications: Often used in residential and commercial heating systems.
Advantages of Boilers
- Efficiency: Boilers are generally efficient in converting fuel into heat, especially in well-maintained systems.
- Reliability: They are reliable and can operate continuously for long periods with proper maintenance.
- Versatility: Can be used with various fuel types and for different applications, from residential heating to large-scale industrial processes.